New markers to make up for the shortcomings of routine screening tests for coagulation:
1、TAT plasma thrombin-antithrombin complex
2、 PIC fibrinolytic enzyme-α2 fibrinolytic enzyme inhibitor complex
3、 tPAI-C tissue plasminogen activator/plasminogen activator inhibitor-I complex
4、 TM Thrombomodulin
TAT and “Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in DIC”
Although TAT is increased in chronic DIC, the overall anticoagulant state can be compensatorily corrected by the liver. TAT is increased in either fibrinolytic-inhibited DIC (early DIC) or hyperfibrinolytic DIC (late DIC), and the increase in TAT is more pronounced because the magnitude of fibrinolytic changes in fibrinolytic-inhibited DIC (early DIC) is small.
In the Guidelines for Pathological Diagnosis of Fibrinolytic-Dominant DIC (2006) of the Academic Standardization Committee of the Japanese Society for Thrombosis and Hemostasis, “TAT ≥20 μg/L and PIC ≥10 μg/mL” are considered necessary for diagnosis. Even in patients with infectious diseases whose platelet count is <120×109μg/mL (and who still have thrombocytopenia), a TAT <7ng/mL suggests a low risk of DIC, and TAT is a marker with a high negative predictive value for predicting the trend of DIC in patients with infectious diseases.
TM and “arteriovenous thrombosis”.
Venous thrombosis has a wide range of triggers, and TAT is significantly elevated in the presence of thrombotic disease. However, the characteristic increase in TAT is not related to the type of thrombus, but rather to the primary disease, especially tumors and severe trauma. For example: in less severe thrombotic load or hypercoagulable state, if TAT is significantly increased, hidden etiology should be considered; in anticoagulant protein deficiency or lupus anticoagulant positivity, if TAT is mildly increased, it suggests that the body mobilizes anticoagulant system; if TAT is at a normal or low level in hypercoagulable/thrombotic patients, it suggests that there is an imbalance/decompensation of anticoagulant function.
The value of TAT for arterial thrombosis lies in dynamic monitoring 24-72 hours after thrombolysis. Arterial thrombosis is a mixed thrombus type with a much lower fibrin load than venous thrombosis, and patients do not initially show a significant increase in TAT. In the early stages of rt-PA thrombolysis, TAT concentration increases significantly, and in the early stages of refocusing, there is a progressive increase in TAT. A rapid decrease in TAT after 2 hours of thrombolysis suggests that the treatment is effective, and a renewed increase in TAT after 36 hours of treatment suggests a risk of reinfarction.
TAT and “VTE complicated by malignant tumor”.
Pathological hypercoagulability and thrombotic risk due to malignancy is present throughout the course of the disease. Accurate identification of patients at risk for VTE and rational use of pharmacologic/mechanical prophylaxis can reduce the incidence of significant VTE. Studies have shown that elevated D-dimer is significantly associated with shorter overall survival in cancer patients, with each 1-fold increase in D-dimer levels increasing the patient’s risk of death (HR) by 1.5-fold, and that elevated levels can be used as a prognostic indicator for assessing the risk of death in patients with brain tumors, lymphomas, breast cancers, lung cancers, gastric cancers, colon cancers, pancreatic cancers, and prostate cancers TAT expression is synchronized with D-dimer metrics, and therefore the clinic is more TAT expression is synchronized with D-dimer index, so the clinic prefers to perform TAT and D-dimer combination test in patients with progressive tumors. A progressive increase in both parameters suggests that patients are at risk of clinical outcome and VTE, and therefore require close attention and timely intervention.
PIC and Acute Ischemic Stroke
The PIC peaks at 3 hours after alteplase injection, and in most patients with a good outcome, the PIC decreases by 50% every 3 hours after 3 hours to almost return to the normal reference range at 24 hours. The peak PIC is variable due to the degree of patient response to alteplase. However, the overall trend is the same in the better healed patients regardless of the degree of peak height. In this experiment, D-dimer and FDP started to decay only after 6 hours, compared with PIC, which lagged behind by 3 hours, mainly due to the fact that D-dimer and FDP are at the end of the fibrinolytic system, whereas PIC intuitively reflects the status of fibrinolytic enzymes. Most of the fatal cerebral hemorrhages occur within 6 hours, so PIC is more useful than the other two within 6 hours, and the combination of PIC, D-dimer, and FDP can quantify the effect of intravenous alteplase on the fibrinolytic system. In patients with a favorable prognosis, intravenous alteplase does not compromise the condition of the vascular endothelium.
tPAT-C and “pathologic pregnancy”.
Physiological hypercoagulability in pregnancy is characterized by a gradual increase in the concentrations of fibrinogen, factors VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, and XII with each week of gestation, and by an increase in the level of vWF in parallel with the concentration of factor VIII. The concentration of anticoagulant proteins decreases to varying degrees; the levels of fibrinogen activation inhibitors (PAI-1 and PAI-2) gradually increase. This hypercoagulability progressively worsens until late pregnancy and lasts until about 6 weeks postpartum, reaching a peak in the puerperium before gradually returning to normal.
Case 1, a 29-year-old woman, was admitted to the hospital with the primary cause of “elevated blood pressure for 2d during the second trimester of labor and delivery at 33+1 weeks gestation. Two days prior to admission, her blood pressure was found to be 190/100 mmHg outside the hospital, and her urine routine indicated that she had urinary protein (4+). Admission diagnosis: (1) pregnancy 2 labor 0 pregnancy 33 +1 weeks (2) moderate preeclampsia. Admitted to the hospital for antispasmodic, antihypertensive, lung promoting treatment, on 2019-11-16 performed cesarean section, delivery of a live baby, intraoperative bleeding 300ml.
Decrease in D-dimer and decrease in tPAT-C in this patient indicated that although vascular injury persisted in the patient but due to termination of pregnancy her chronic DIC process was arrested and hyperfibrinolysis was alleviated, this patient was at low risk of hemorrhage and DIC.
tPAI-c and PIC for “Intraoperative Cesarean Hemorrhage” Identification
Previously, it was difficult to differentiate fibrotic hyperactivity secondary to DIC from primary fibrinolytic tPA-induced hemorrhage, and thromboelastography was required. At this stage, tPAI-c and PIC can be used as indicators to differentiate, i.e., increased PIC indicates secondary fibrillar hemorrhage caused by DIC, and tPAI-c indicates primary fibrinolysis. However, whether this index is representative and has the same effect as thromboelastography needs more observation.
tPAI-c Associated with “Obesity
The endocrine effects of adipose tissue release PAI-1, activate platelets and coagulation, and release PAI to inhibit fibrinolysis, and PAI is higher in the plasma of severely obese patients. An obese patient after liver transplantation developed multisite portal vein thrombosis because he did not receive adequate anticoagulation. The patient had poor blood flow in the right limb, and D-dimer continued to fall after administration of low-molecular heparin. However, the patient’s tPAI-c was still at a high level. Genetic testing revealed that the patient had a 4G4G mutation in PAI-1, and the continued high level of PAI-1 led to a compensatory increase in tPAI-c. The patient’s indexes were normalized after further increase of anticoagulant drugs warfarin and rivaroxaban.
tPAI-c and “cancer”.
Metastasis of cancer cells in the bloodstream can have an impact on local and even systemic fibrinolysis, especially on the formation of tumor thrombi in the abdominal wall. TPA is released from the tumor plugs that are affixed to the vessel wall to form local fibrinolysis and dissolve fibrin, which causes the tumor cells to affix to the vessel wall, thus further metastasizing to other organs. As a result, tPAI-c is elevated in patients with tumor bloodway metastasis.
TM and “New Crown Pneumonia”
Many patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in neocoronary artery disease (NCA) have systemic inflammation and cytokine storms, the most typical indicator of which is elevated TM. There is also a combination of multiple organ failure and extensive vascular injury due to various causes of DIC, at which time the concentration of TM in the blood increases. It is worth noting that in the presence of acute renal failure, with damage to renal function, TM is significantly elevated. With non-acute renal impairment, there is no significant elevation of TM because TM can be excreted in the urine. Therefore, the perception of TM should be assessed holistically, taking into account renal function.
TM and “sepsis”
In sepsis, if there is a severe infection that leads to DIC combined with multi-organ failure, the mortality rate is very high without controlling the primary disease, only coagulation interventions.TM plays an important role in sepsis, and in septic DIC the amount of thrombin generation is very alarming, and vascular damage causes a lot of structural disintegration of the TM because of the very high content of prothrombin, and in the case of stimulation the very high level of thrombin turns mostly into thrombin, not vascular damage. Most of the prothrombin becomes thrombin, which is not completely acceptable to the TM on the endothelial surface of the blood vessel. Vascular damage causes a massive disintegration of the TM structure, and there is less and less effective TM, and less and less of the TM can really work on the cell membrane, and this process slows down the course of the disease, and the process will not be too long-lasting if there is no human intervention, so there is now an artificial reorganization alternative therapy, but the success or not is still in the clinical trial.
| Abbreviation | English Name | Reference range |
| TAT | Thrombin-antithrombin complex | <4 ng/mL |
| Clinical significance | Molecular marker of the activation of the coagulation system, suggesting activation of thrombin and the beginning of thrombus formation.
1、Confirms the generation of thrombin, a marker for the activation of the coagulation system; 2、It suggests DIC or excludes DIC; 3、Elevated concentration can predict the early formation and degree of thrombus; 4, the effect of anticoagulation therapy determination, especially after thrombolytic therapy rethrombosis monitoring. |
|
| PIC | Fibrinolytic-α2 fibrinolytic inhibitor complex | <0.8μg/mL |
| Clinical significance | Reflecting the early marker of fibrinolytic system activation, suggesting that fibrinolytic enzymes are activated and thrombus has formed.
1、It is suitable for the early diagnosis of DIC and pre-DIC state, and guides the treatment of DIC; 2、Clinical specific diagnostic index of common thrombophilia (VTE); 3、Elevated time warning of all kinds of major surgery, malignant tumor-induced thrombosis, and speculate on the progress of the disease; 4, monitoring of anticoagulation and thrombolytic therapy. |
|
| TM | Thrombomodulin | 3.8~13.3 TU/mL |
| Clinical significance | Marker of vascular endothelial cell damage, suggesting that the vascular endothelium is damaged.
1、It has the function of capturing thrombin, anticoagulation and anti-inflammation, judging the damage or recovery of vascular endothelium; 2、Elevated concentration suggests endothelial system damage, impaired renal function, DIC; 3、Elevated TM predicts the occurrence and progression of atherosclerosis. |
|
| t-PAI-C | Tissue plasminogen activator – plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 complex | Male <17ng/mL
Female <10.5ng/mL |
| Clinical significance | A combination of molecular markers reflecting damage to the fibrinolytic system and vascular endothelial cells, suggesting that the cause of the disease has not been removed and thrombosis is ongoing.
1、One of the best diagnostic indicators of venous thromboembolism (VTE); 2, Risk indicator for myocardial infarction; 3, To determine the degree of repair of the vascular endothelial system after surgery and to monitor the effect of thrombolytic drugs. |
|
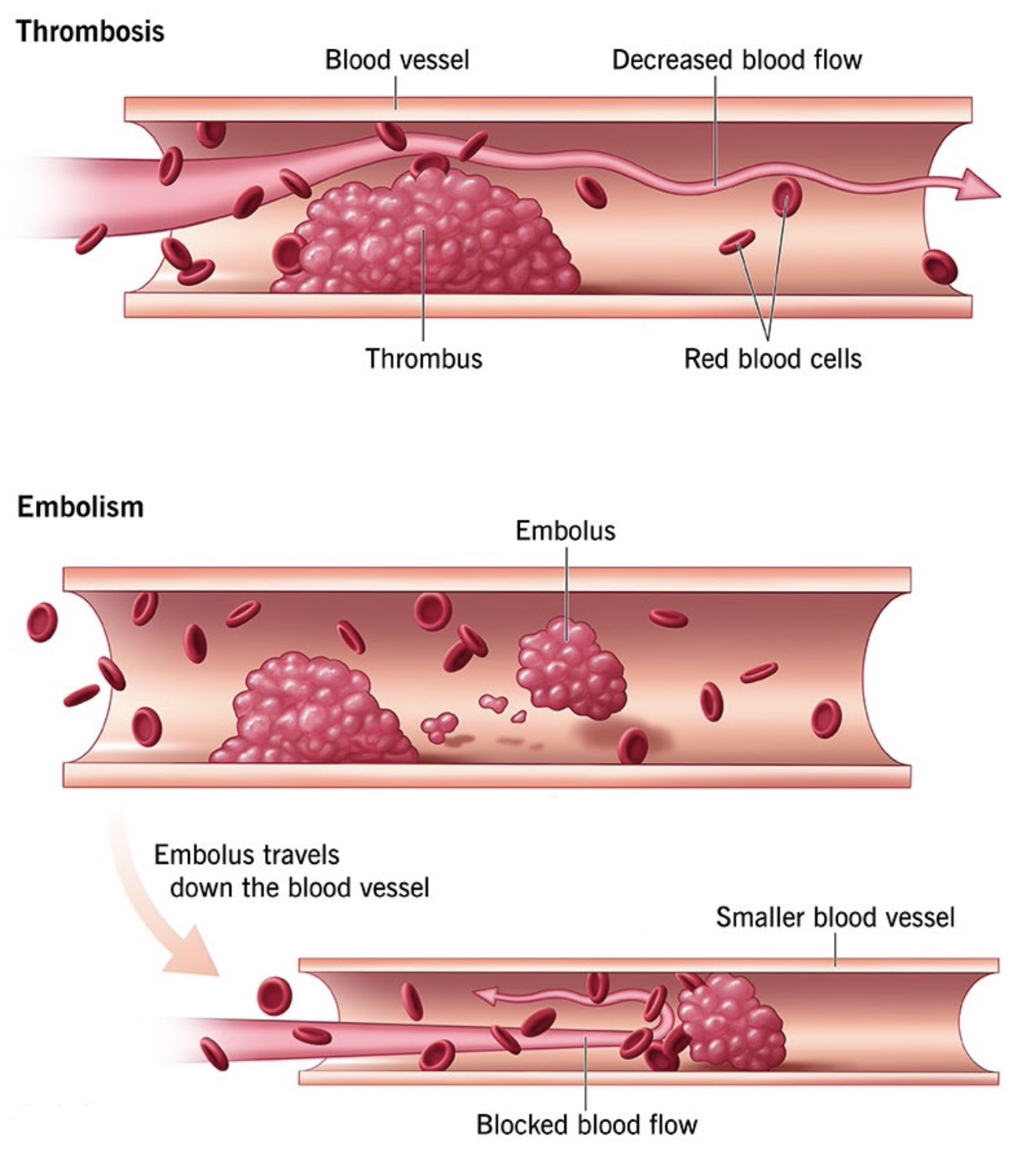
Thrombosis is a high-mortality disease with an insidious onset and a sudden onset. Whether it is arterial thrombosis, venous thrombosis, or microvascular thrombosis, it poses a great threat to human health. A number of studies have shown that early detection and diagnosis of people at high risk of thrombosis in various clinical departments can realize early intervention, early treatment and effectively reduce the harm of thrombosis to human health.